Battery saver active — causes and fixes
Extend your device's battery life using the active battery saver feature.

Your car’s dashboard lights can tell you about a higher operating temperature, ABS faults, and even troubles with the engine. However, you might be stunned to see the battery saver active as you sit behind the wheel.
The battery saver mode was designed for most General Motors and Chevrolet models, and it notifies you of battery problems. Still, many things can cause your board computer to switch to a battery saver mode. This guide will lead you through them all, so you can figure out the root cause of your battery issues.
What’s battery saver mode and what does it mean?
The battery saver mode turns on once the battery sensor informs the engine control unit (ECU) computer of an improperly charged battery. If you notice this message written on the board, you should expect several changes in your car’s electrical systems.
The mode is designed to get you going as much as possible if problems with battery charge occur on the road. So, this mode allows you to reach a mechanic or a car electrician without having to tow your car. While that’s a good thing, you might not expect this mode to shut off all of your electrical systems that aren’t essential.
So, this mode might render your car’s radio, interior lights, or even climate control options useless. It does it to prevent further battery drain caused by these features. If you happened to experience a battery discharge warning present on the dashboard before, it could have caused the battery saver mode.
It’s not the only thing that turns on the battery saver mode, but it’s usually something related to your car’s battery and its inability to hold the charge.
Checking battery voltage
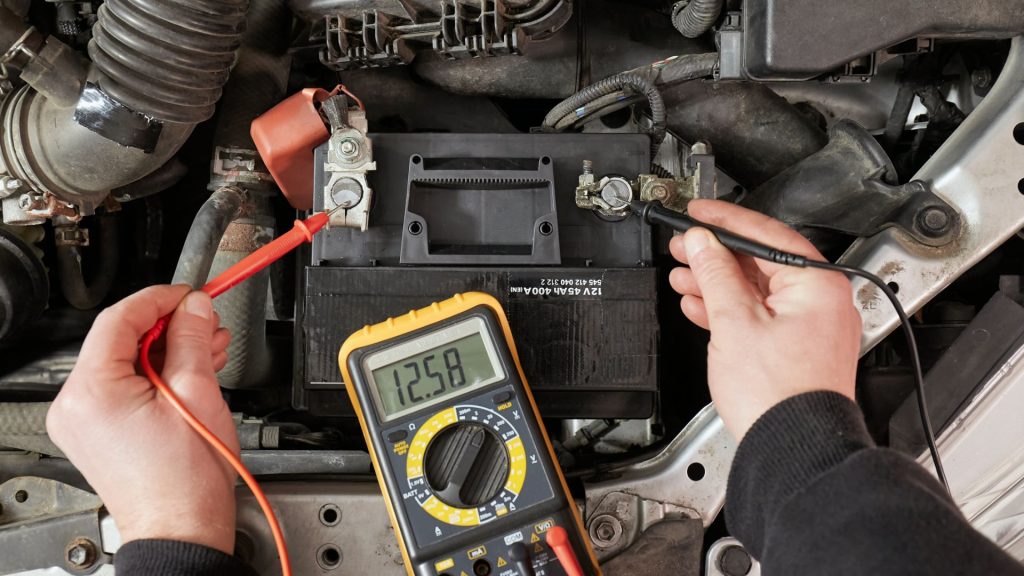
Before you drive your car to an electrician, you should check your battery charge. Even though the battery saver mode is displayed on your board computer, you should test the voltage yourself. A bad battery sensor could simply cause inaccurate readings, triggering the battery saver mode.
This sensor is located on the negative terminal of your battery, and it measures the battery voltage and reports it to the computer. So, you can use a voltmeter to put the sensor’s efficiency to a test. Remove the positive and negative terminal covers, and attach the voltmeter’s leads accordingly.
The positive lead goes on the positive terminal, and the negative lead goes to a negative terminal. Next, measure the battery charge and compare the readings. Usually, the battery sensor readings of below 12.4 volts trigger the battery saver message.
If the mode turns on, and your voltage measurements reach 13 volts or more, you could be dealing with a damaged sensor. It’s not a rare sight, so replacing the sensor will fix the problem in this case. It’s always worth checking if the sensor works properly to avoid having to needlessly pay for expensive repairs.
Problems that trigger battery saver mode

If you check your battery charge and it’s not a sensor fault, it’s time to deal with possible reasons behind the mode activation. You shouldn’t drive for too long when this mode activates regardless of the cause. Here are some of the most common reasons behind the battery saver mode:
- Battery problems
- Damaged battery connections
- Bad alternator
Another possibility is that parasitic battery draw has caused drainage and that’s the reason behind a low voltage reading. The parasitic draw occurs if your battery keeps getting drained even after shutting the engine off.
Of course, if you leave your headlights on during the night, it will empty the battery. However, other electrical features might still be working after you park your car and drain the battery. Perhaps you didn’t close the glovebox compartment or the trunk properly. This would cause interior lights to still glow and it will result in a parasitic draw.
Also, bad switches and connections might cause features like your radio to still work even after you exit the car. Make sure to check for parasitic draw first before you blame the problem on your battery or alternator.
Problems with the battery
Battery problems are the first that come to mind in this case, and you can confirm them by using a voltmeter. Still, if your battery is getting old, the cells might degrade and it will cause the inability to hold the charge for a long.
This can be a real problem, especially when combined with running daily errands that all require taking short drives. Your alternator charges the battery as you crank the engine, so if you don’t drive for enough time for it to charge the battery properly, it will result in battery saver mode.
This happens more often as the battery gets older and degrades, so you should have an electrician examine it. Driving for about an hour should help determine the problem since it should be enough for your alternator to charge the battery. However, it’s not always worth risking it with a battery saver mode being on, so inspecting the battery can be a safer option.
Damaged battery connections
Battery cables and connections can also be the reason behind the battery saver mode activating. You can inspect a good part of those connections yourself. Take a look at the terminals to see if they are corroded, or if a few bolts need to be tightened up.
In most cases, replacing the damaged cables and tightening up the bolts can save your battery and restore it to a factory shape. You can also try using different cleaning agents to remove the corrosion from the battery terminals. If done right, this can shut down the battery saver mode.
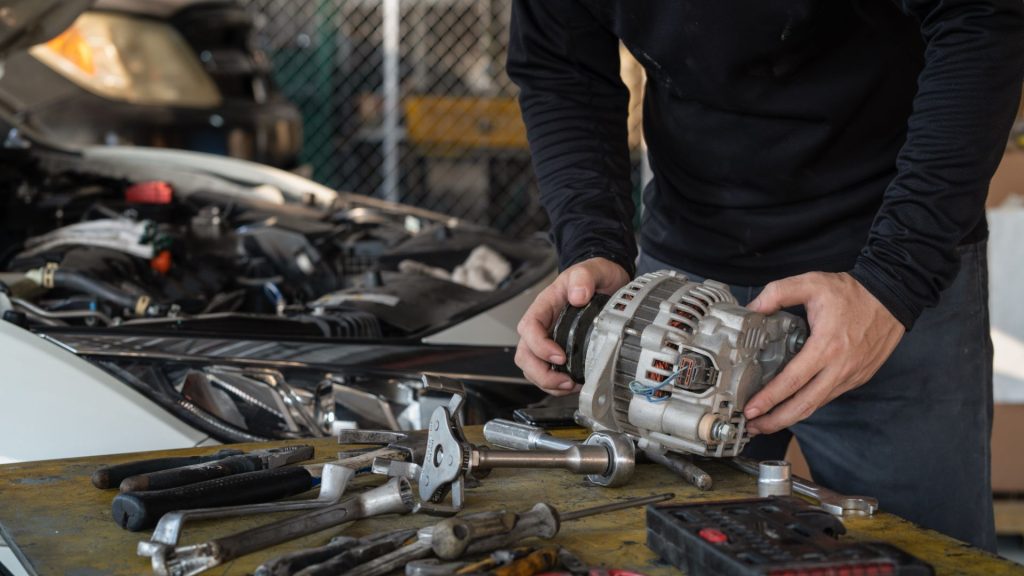
Bad alternator causing the battery saver
You probably know that the battery provides electrical power for all of your car’s features. However, the alternator serves an important role in charging the battery as you drive. If the alternator fails, your electrical features will be charged solely by the battery.
Eventually, the battery will be depleted, but this time, the alternator won’t be able to charge it the next time you crank your engine. While you can jumpstart a car with a bad alternator, that’s not always the solution.
Sometimes you’ll need to replace it if your battery wasn’t completely drained by the lack of charge. If your car stalls soon after you start it, and you notice growling noises accompanied by the smell of burning rubber, it’s a bad alternator. It’s often the cause of battery saver mode activating since the battery will drain excessively if the alternator isn’t working.
Our take
Overall, the battery saver active warning gives you just enough miles to reach an electrician and inspect the battery and electrical system. While it can be just a result of a bad sensor, it still deserves to take a closer look at the battery, alternator, and cables.
Don’t risk your car stalling on the road by driving for too long with the battery saver mode active.
Does battery saver mode mean I need a new battery?
Battery saver mode means you need a new battery if it got too depleted or if it can’t hold a charge anymore. However, it might require replacing the alternator or the battery cables instead of a battery.
Can I drive with the battery saver active?
You can drive with the battery saver active for a while, but it’s safer to drive straight to a mechanic or electrician to examine the car’s battery and electrical connections.
How long can you drive your car in battery saver mode?
You can drive for about 100 miles or slightly more in a battery saver mode, but there’s no particular limit. Your car can run on battery alone up to the maximum of 200 miles if the failed alternator is causing the battery saver mode.
What does battery saver active mean on Camaro?
The battery saver active on Camaro means your battery charge has dropped below 11.7 volts, so you won’t be able to drive for much longer and your electrical features will shut down.
What does battery saver active mean on Cadillac?
The battery saver active on Cadillac means your car is running on battery power alone, or that the sensor or alternator has malfunctioned.