Clutches in automatic transmissions — explained
Explore clutches in automatic transmissions.
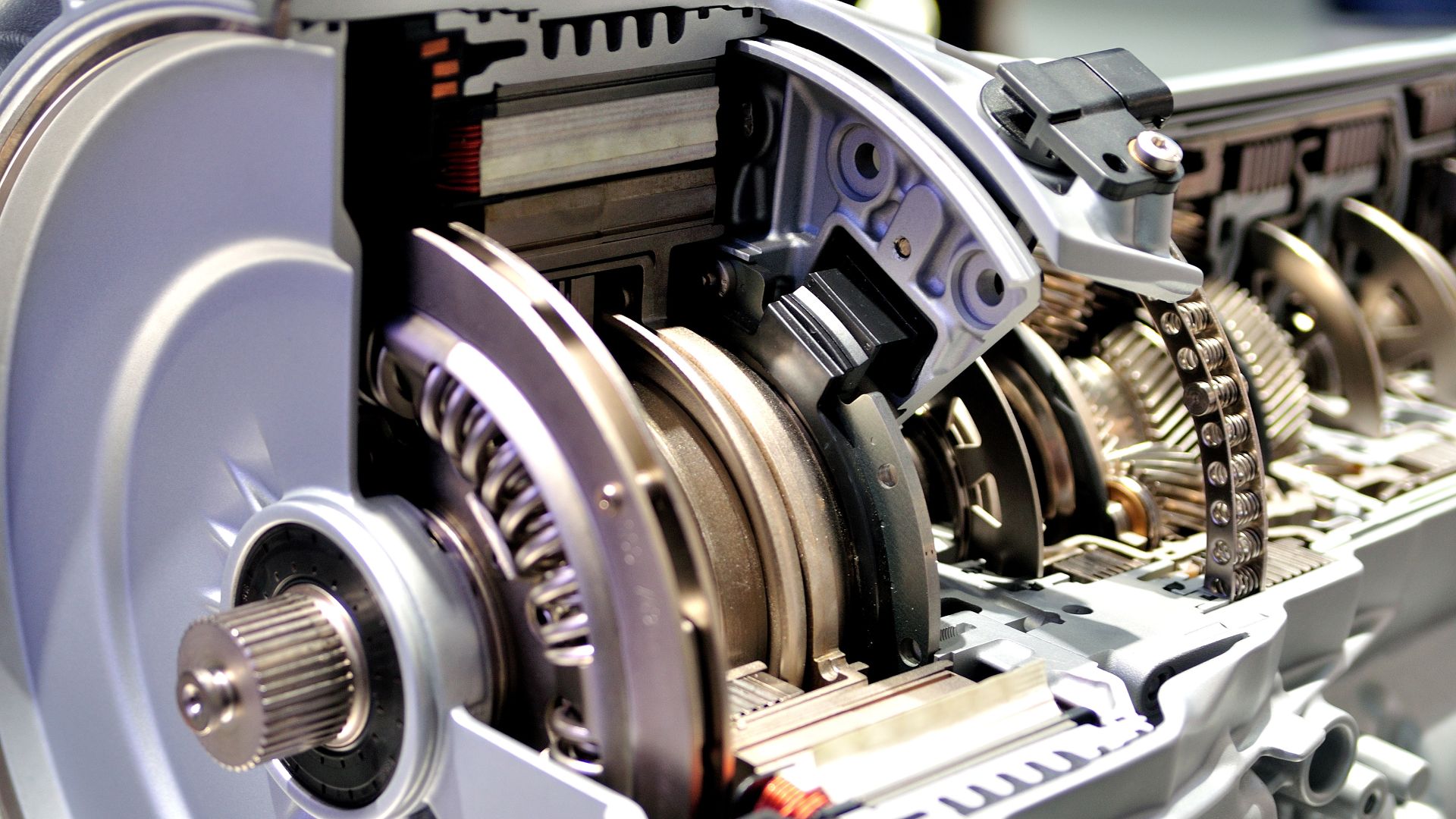
Most of the time, we think of a clutch in the context of a manual transmission, but automatic transmissions also have a clutch system. Whether your car has an automatic or manual transmission, it relies on a clutch to control the link between the gears and the engine.
Transmissions are necessary for any vehicle to prevent the engine from destroying itself. Without a gearbox system, automobile engines would spin too quickly for structural stability, which would cause the majority of engines to break apart or overheat.
Additionally, any vehicle lacking a transmission would be unable to use the engine’s speed, limiting the vehicle’s maximum speed. This article will look at how vital a clutch is, its types, and how clutches in automatic transmissions work.
What is an automatic transmission?
One of the most complicated components in your vehicle is the transmission, a metal case that houses a series of gears – which explains its nickname “the gearbox.” The transmission takes power from the engine and delivers it to the wheels to help power your vehicle. It ensures the right amount of energy goes to the wheels to operate at a given speed.
In a manual transmission, the driver is responsible for shifting the gears, while in a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the car does the shifting for you. So the question becomes, to shift or not to shift?
There are two significant differences between an automatic transmission and a manual transmission:
- There is no clutch pedal in an automatic transmission car
- There is no gear shift in an automatic transmission car
Once you put the transmission into the drive, everything else is automatic. Automatic and manual transmissions accomplish the same, but they do it differently.
What is the function of automatic transmission?
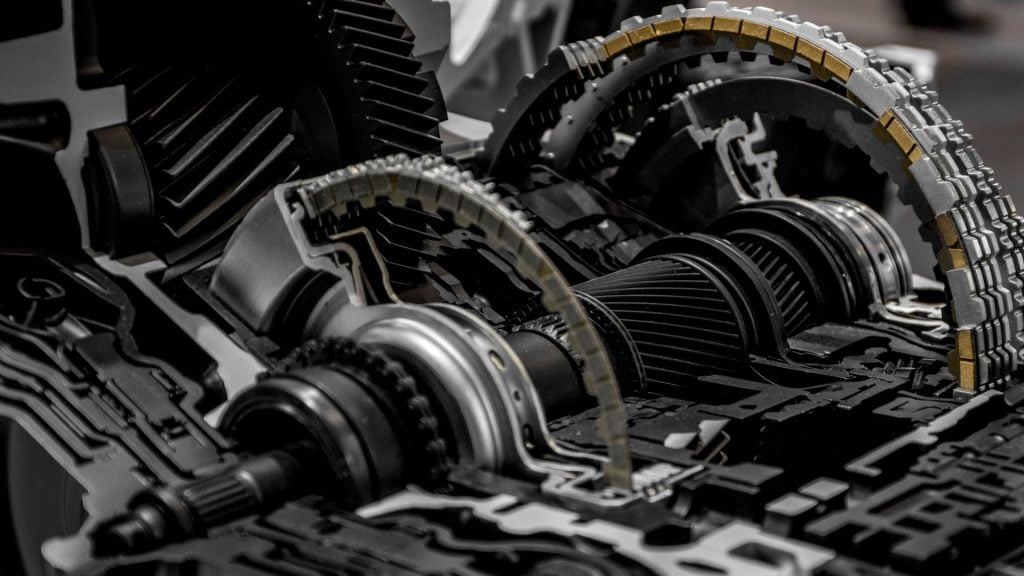

The primary function of an automatic transmission is to provide a wide variety of output speeds while allowing the engine to run within its limited speed range. Without a gearbox, there would only be one gear ratio available for cars, and that gear ratio would need to be chosen for the vehicle to reach the necessary top speed.
The transmission employs hydraulic fluid pressure to regulate which gear is engaged when power enters the transmission. The gearshift is involved; small tubes that direct fluid pressure to the proper spot are opened and closed by a valve body.
To pick the proper gear for the engine speed and the pace you are traveling, sensors decide where to direct the fluid pressure, and the automatic transmission in your car shifts into the first gear, which is the lowest when you press the start button.
Automatic transmission makes use of a torque converter. The torque converter’s turbine is powered by transmission fluid, which is created as the engine transfers power to the torque converter’s pump. This device boosts the fluid’s power and moves it back to the turbine, spinning the latter and its linked central shaft.
However, the transmission must shift gears to accelerate to higher speeds. This helps with fuel efficiency and keeps engine RPMs down. To shift into the next gear while your car is moving, one gear must be disconnected. Clutches serve that purpose. Because of all this, low transmission fluid symptoms or torque converter issues should be taken seriously as they can reduce the efficiency of the transmission.
Automatic clutches
An automatic clutch is a feature of an automatic transmission. Built-in sensors, processors, and controllers operate the clutch at the ideal moment based on your current speed, the amount of accelerator pressure applied, and other parameters rather than relying on human control, which enables drivers to concentrate on other duties while driving.
While operating a car with an automatic transmission, you can hear it in action. Your engine will get louder when you apply more pressure to the accelerator; the torque converters’ built-in sensors will detect the change and cause an automatic transfer to a higher gear.
How do clutches work in an automatic transmission?
A drum-shaped clutch pack made up of multiple discs is found inside an automatic transmission. In an automatic transmission, a piston inside the drum uses oil pressure to force the clutch pack together, locking the clutch pack’s parts together to facilitate gear shifts.
A pressure plate is the most important component of the entire clutch assembly. The driven friction disc is held between the pressure plate and the flywheel by a clamping force (pressure) applied by the pressure plate. The pressure plate and flywheel revolve in tandem because bolts hold them to each other. A diaphragm or springs in the pressure plate apply pressure to the driving surface or central casting. The primary casting can rise off the driven disc when the diaphragm or clutch levers are activated to release or disengage the drive.
With an automatic transmission, there are multiple clutches. Different planetary gears powered by the hydraulic fluid can be engaged and disengaged using various clutches. The clutches are locked via uniformly spaced ridges that engage the clutch housing and gears. Using the exact spring mechanism as the manual transmission, the fluid pressure level decides which clutches are engaged. Due to the differences when compared with manual transmission clutch, there’s no pedal and drivers can’t be riding the clutch or improperly using the pedal.
Types of automatic transmission

However, there are different automatic transmission that also determines the function and kind of clutches an automobile uses. Below are a few details of the most common automatic transmission in use;
Triptronic transmission
Triptonic transmission is an example of an automated transmission that works similarly to a manual gearbox. However, it differs from manual operation in that a torque converter is used in place of a clutch pedal, and the driver does not have complete control over the gears.
The ability to override the automatic mode makes this device special. It entails that you can operate your vehicle automatically while also having the option to switch to manual mode when necessary, such as ascending a hill or descending a steep route.
Dual-clutch transmission
A dual-clutch transmission, which combines an automatic and manual transmission, lacks a torque converter. Instead, it employs two different shafts with their clutches, one for odd-numbered gears and one for even-numbered gears, to change the gears.
While shifting between lower and higher gears is seamless; they can become noisy and move clumsily after some wear and tear. As a dry transmission, the DCT never requires the driver to replace the gearbox fluid. It causes the clutches to become dry and finally lose their frictional strength.
Traditional automatic transmission
This type of automatic transmission also referred to as a torque converter automatic, is the one that can be found in the majority of cars nowadays.
It does not use a clutch transmission to shift gears, unlike a manual gearbox. Instead, a torque converter or a hydraulic fluid coupling does this function. It enables good vehicle management and is connected to the engine’s electronic control.
Automated-manual transmission
This form of automatic transmission often referred to as a semi-automatic transmission (SAT), uses a standard clutch and gear configuration but automates the action using sensors, actuators, processors, and pneumatics.
The performance of the vehicles equipped with this transmission is superior on highways. They are not advised for city driving since, under hard acceleration, the engines seem jerky.
How many clutches are in an automatic transmission?
There are three main clutches in an automatic transmission. A malfunction with any of the two bands or three clutches inside an automatic transmission can affect your car’s performance and driveability.
Different gears are connected and detached when these clutches and bands engage and disengage to transform energy into movement. Let us take a look at the functions of these different clutches below.
Hydraulic clutches
Utilizing hydraulic fluid (such as oil), hydraulic clutches extend and retract pistons to engage and release the clutch. They are appropriate for hydraulic systems where the rotational speed must be predetermined or constant for engagement and disengagement.
Centrifugal clutches
When the appropriate rotational speeds are attained, centrifugal clutches automatically engage and disengage. They work well in applications that call for engagement and disengagement at constant or variable rotating rates.
Electric clutches
Electrical energy is transformed into mechanical energy by electric clutches. An electromagnetic field is created when a current from the power source is passed through it, and a pressure plate is drawn to the electromagnetic field that engages the clutch.
When the current from the power source stops flowing, the clutch releases. These clutches are appropriate for usage in situations where engagement and disengagement must take place with a conveniently available power supply and at a particular or constant rotating speed.
Signs of a bad clutch
There are several indicators that the clutch in your car needs repair. The earlier you can identify a clutch repair or failing clutch, the more likely you might avoid more damage repairs.
Slipping clutch
When your car’s rpm rises, your engine becomes noisier as the gas pedal is depressed. Still, the vehicle is not accelerating as quickly as it should, which is the main sign of a faulty clutch in an automatic transmission.
Difficulty changing gears
You will observe that the gears move smoothly and without resistance if your clutch and gearbox are in excellent shape.
To enable a simple transfer to the next gear, the clutch’s function is to release the tension between the engine and the transmission. Changing gears will be more challenging if the clutch fails to remove the connection between the engine and gearbox.
It frequently occurs in all gears when the clutch the gearbox is damaged, so if you’ve observed that shifting into and out of gear in your gearbox car has gotten challenging recently, it’s time to check the clutch.
Clutch feels soft while pressing
In older or more powerful automotive models, the clutch assembly is frequently extremely heavy, and pressing the clutch pedal requires some force.
When the clutch pedal feels incredibly softer than usual, there may be an issue with the clutch’s pressure plate.
Our take
A clutch is a crucial part of an engine because it can disengage and engage the driving and the driving member and transmit motion from one machine part to another. A clutch is necessary for separating a car’s engine and wheels, in light of the judgment made above. While an automobile’s wheels do not revolve constantly, its engine does.
However, poor driving conditions can seriously shorten the clutch’s life and rapidly cause damage. We advise that you take good care of your vehicle to enjoy a smooth ride.
Do automatic transmissions have clutches?
Yes, automatic transmissions do have a clutch, but the clutch is implemented differently than in a car with a manual transmission.
What type of clutches are used in an automatic transmission?
Automatic transmission make use of either dry clutches (for DCT) or wet clutches(for DSG), depending on the engine torque.