Constant-velocity joint definition and meaning
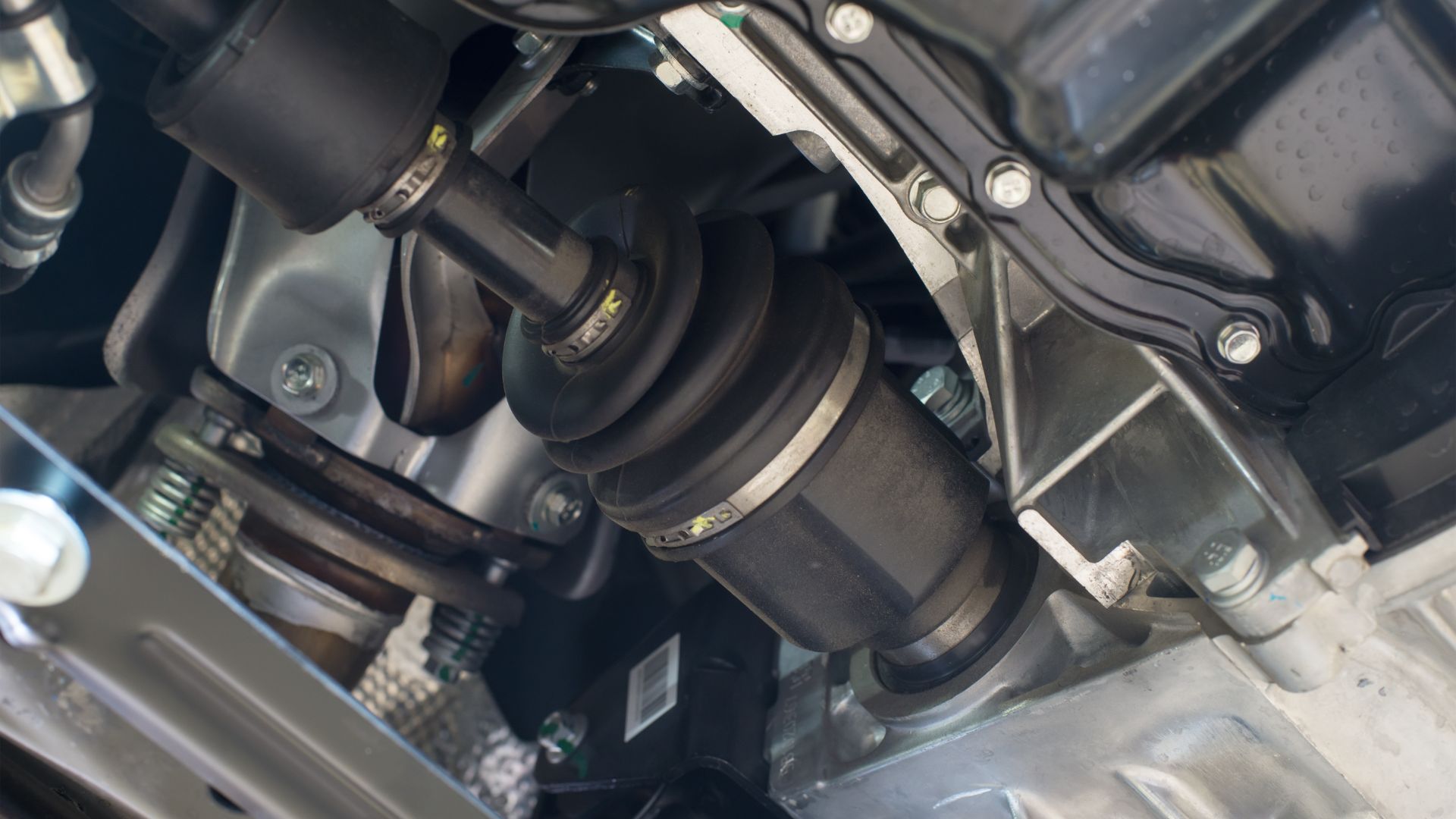
The constant-velocity joint, also known as CV joint, is a type of joint used in cars and other vehicles to connect the shaft of a wheel to the drivetrain. The CV joint allows the shaft to rotate at a constant speed even when the wheels are turned, making it an essential component for smooth car operation. There are two types of CV joints: inner and outer. The inner CV joint connects the driveshaft to the wheel hub, while the outer CV joint connects the wheel hub to the suspension. Both types of CV joints are protected by a boot that helps keep dirt and debris out. Over time, however, these boots can tear or leak, causing damage to the CV joint. This can lead to a loss of power or even a complete breakdown of the drivetrain. Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent this type of damage.